-40%
Classic Sigillaria boblayi coal age extinct lycopod Carboniferous fossil plant
$ 6.33
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
I combine shipping costs.Each item is different, so please wait with payment after purchase -
I will send You a combine invoice.
Usually, it will be cost of shipping the heaviest item.
Specimen
:
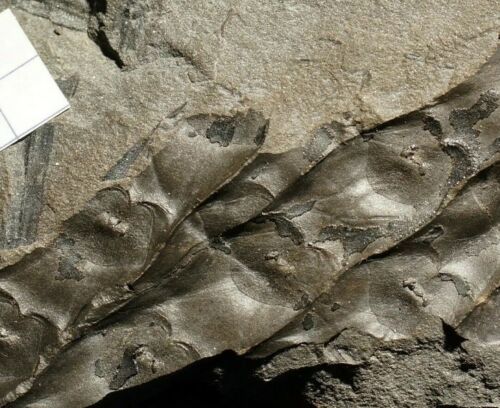
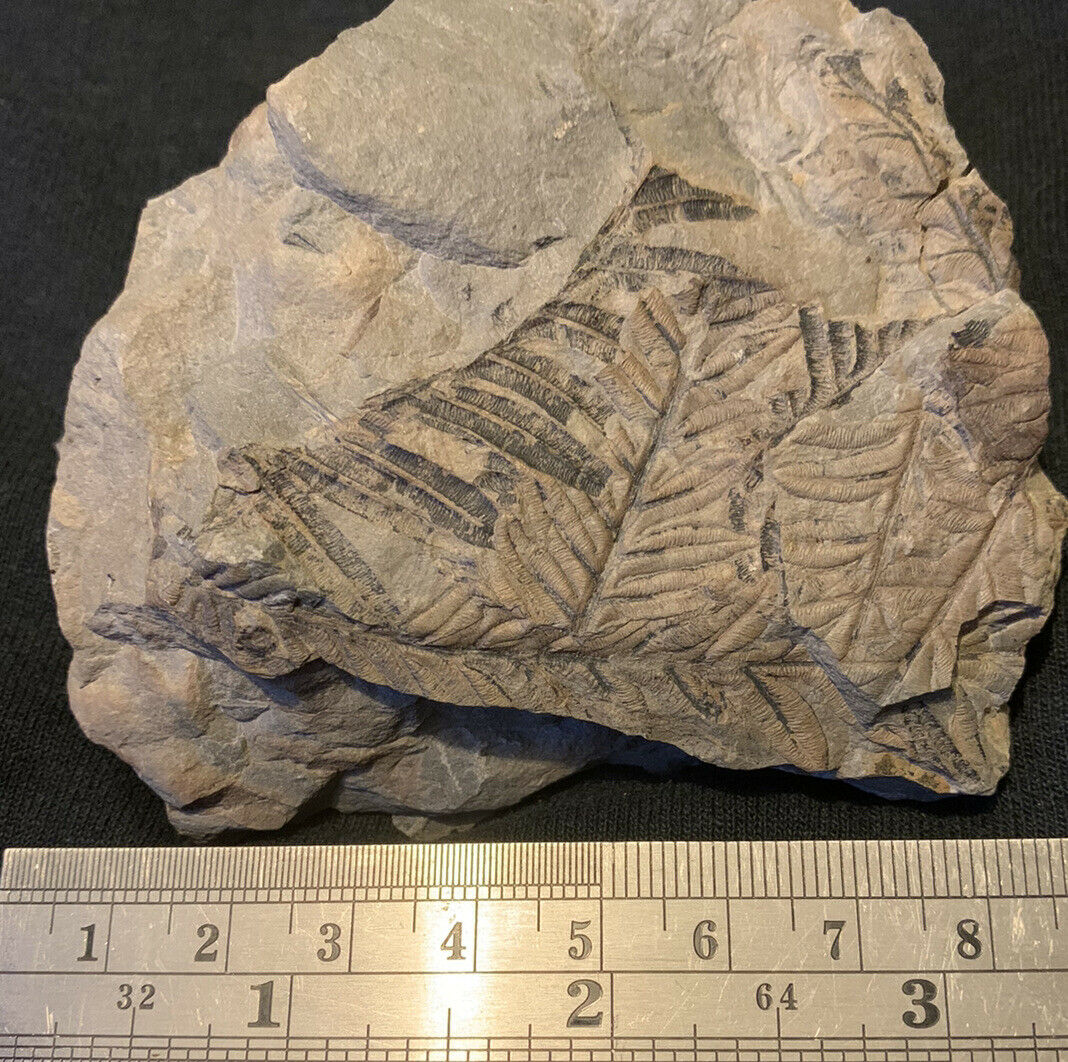
Sigillaria boblayi
Brongniart 1828 - very nice, rare classic Upper Carboniferous coal swamp lycopod fossil
Locality:
Poland, GZW Upper Silesia Coal Basin
Stratigraphy:
Upper Carboniferous - Pennsylvanian / Westphalian B - Orzeskie Beds
Age:
ca. 310 /3 15 Mya
Matrix dimensions:
ca. 11,0 x 6,0 x 1,9 cm / white square on last pictures is 1,0 x 1,0 cm
Description:
Sigillaria
is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants which flourished in the Late Carboniferous period but dwindled to extinction in the early Permian period. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate Lepidodendron. Sigillaria was a tree-like plant, with a tall, occasionally forked trunk that lacked wood. Support came from a layer of closely packed leaf bases just below the surface of the trunk, while the center was filled with pith. The old leaf bases expanded as the trunk grew in width, and left a diamond-shaped pattern, which is evident in fossils. The trunk had photosynthetic tissue on the surface, meaning that it was probably green. The trunk was topped with a plume of long, grass-like, microphyllous leaves, so that the plant looked somewhat like a tall, forked bottlebrush. The plant bore its spores (not seeds) in cone-like structures attached to the stem. Sigillaria, like many ancient lycopods, had a relatively short life cycle - growing rapidly and reaching maturity in a few years.
Some have suggested that Sigillaria was monocarpic, meaning that it died after reproduction, though this is not proven. It was associated with Lepidodendron, the scale tree, in the Carboniferous coal swamps. The clubmoss trees of the genus
Sigillaria
formed an important part of the coal swamps in the Late Carboniferous. They could reach a height up to 30 ms and bore grasslike leaves in the upper part of the unbranched or once divided trunk. The leaves were attached directly to the stem and they left scars when they were shed. Characteristic of the genus of
Sigillaria
is the fact that the leaf scars were arranged in vertical rows. On the ground of these leaf scars many species have been described. The trunk was somewhat thickened at the base.The spore-cones were attached in or under the crown directly to the stem. They are called
Sigillariostrobus.
The underground parts of the tree can hardly be distinguished from those of
Lepidodendron
and they are called
Stigmaria
. From the Westfalian D on the number of species of
Sigillaria
diminished strongly.
Systematic:
Division:
Tracheophyta (Lycoposida)
Class:
Lycopodinae
Order:
Lycophodiales
Family:
Subsigillariaceae
Genus:
Subsigillaria
Species:
Sigillaria boblayi
BRONGNIART 1928